Skin Anatomy
The skin is the largest organ of the body, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin protects us from microbes and external aggressors, helps regulate body temperature, and permits the sensations of touch, heat, and cold.
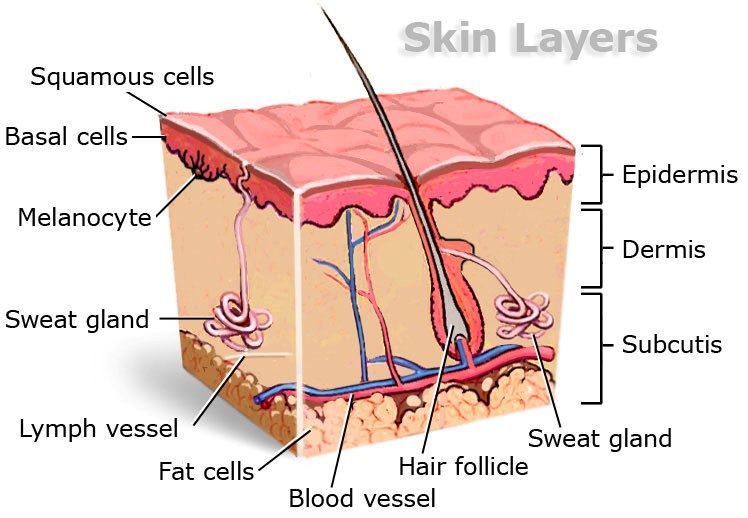
Skin has three layers:
- The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone.
- The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
- The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue.
The skin’s color is created by special cells called melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin. The human skin is the outer covering of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs.Human skin is similar to that of most other mammals.Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin. The adjective cutaneous literally means “of the skin”.
Skin Types
Normal skin
Normal skin displays a smooth texture and a rosy, clear surface, with fine pores. There are no visible blemishes, greasy patches or flaky areas. Sebum production, moisture content, keratinisation and desquamation are well-balanced. Normal skin is often found in young persons. This is the least problematic skin type as the moisture content of your skin and production of oil is perfectly balanced.
Oily skin
Oily skin is characterized by an increased amount of lipids on the skin surface due to overactive sebaceous glands. It is shiny and thick, often with enlarged pores. Oily skin is prone to blackheads and other blemishes. It occurs more often in men than in women, and it predominantly affects adolescents and younger persons. An oily skin is greasy and shiny.
Dry skin
Dry skin is characterized by a lack of moisture in its corneous layer, resulting in tightness and even flaking. The skin appears dull, especially on the cheeks and around the eyes. It may lack elasticity, with accentuated fine lines and wrinkles. In more severe cases, itching and burning may occur. Extremely dry skin shows signs of cracking and fissuring. The most common characteristic if you have dry skin is your skin is dry and flaky. Your skin feels tight and you’ll have finer pores and finer lines. Having dry skin can increase skin irritation. Dry skin can be genetically determined or triggered by factors such as cosmetics, climate and medications. It can be a natural consequence of the ageing process, as sebum production slows down.
Sensitive skin
Sensitive skin is not a skin type, but rather a symptom caused by various factors. Patients tend to describe their skin as “sensitive” if it frequently reacts with redness, itching, burning or dryness to the topical application of skin care products. Causes for this condition may be an underlying skin disorder, allergies, contact to irritants in certain products, or the use of inadequate, not skin type-adjusted products. Most commonly, the facial skin is involved.
Skin Care
Cleansing
Proper cleansing to remove dirt, makeup and pollution should be the core of every skin care routine. Try to wash your face twice daily, usually in the morning and then again before going to bed at night. Use ALLUSHYNE face wash and simply use water and a soft face cloth (its a moisturizing, gel-based cleanser.) Use lukewarm water to keep irritation to a minimum and avoid harsh cleansers, even if your skin is oily.
Toning
Toners with skin-replenishing ingredients hydrate, refresh and revitalize the skin’s surface immediately after cleansing. They also help diminish the look of redness and dry patches.
Exfoliating
Environmental damage causes the surface of the skin to become dull, rough, and uneven. Exfoliating eliminates this build up, which otherwise would cause clogged pores, uneven skin tone, and worsen the appearance of fine lines and deeper wrinkles and pigmentation.
Skin Conditions
There are various types of skin conditions. The best way to treat these conditions is to consult with specialist healthcare professionals for best and long-lasting effects.
Fungal infections
Fungal infections of the skin are very common and include athlete’s foot, jock itch, ringworm, seborrheic dermatitis, and yeast infections.
Hair loss
Hair loss, or alopecia, is a concern for men, women, and children.
Acne
Acne vulgaris, also known as acne, is a long-term skin disease that occurs when hair follicles are clogged with dead skin cells and oil from the skin. Acne is characterized by areas of blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and greasy skin, and may result in scarring.
Acne commonly occurs in adolescence and affects an estimated 80–90% of teenagers. During puberty, in both sexes, acne is often brought on by an increase in hormones such as testosterone. Excessive growth of the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes, which is normally present on the skin, is often involved.
Acne severity classification as mild, moderate, or severe helps to determine the appropriate treatment regimen. Typical features of acne include seborrhea (increased sebum secretion), micro comedones, comedones, papules, nodules (large papules), pustules, and in many cases scarring.
Urticaria
a rash of round, red weals on the skin which itch intensely, sometimes with dangerous swelling, caused by an allergic reaction, typically to specific foods.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by sun damage, inflammation, or other skin injuries, including those related to acne vulgaris. People with darker skin tones are more prone to hyperpigmentation, especially with excess sun exposure.
Many forms of hyperpigmentation are caused by an excess production of melanin. Hyperpigmentation can be diffuse or focal, affecting such areas as the face and the back of the hands.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a condition in which the pigment is lost from areas of the skin, causing whitish patches, often with no clear cause. Healthy beauty: Healthy beauty is all about smart, scientifically sound ways to care for and enhance your skin, hair, nails and body.
Eczema
Eczema is term for a group of medical conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed or irritated.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a common skin disorder that produces thick red plaques covered with silvery scales.
Cold sores
You might hear them called fever blisters — are proof that life can be unfair. Some people get them, others don’t. They’re itchy and painful, and they can make you feel self-conscious. But there are ways to treat and prevent them.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a common disorder that mainly affects skin on the face. It causes redness on the nose, chin, cheeks, and forehead.
Lice
Lice are tiny insects that live on humans and feed on blood. When a large number of lice live and multiply on a person, it is called an infestation.
Poison ivy
Poison ivy, oak, and sumac are plants that can cause a red, itchy rash called allergic contact dermatitis . It is the most common skin problem caused by contact with plants.
Shingles
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a viral infection caused by the chickenpox virus. Symptoms include pain and a rash on one side of the body.
Skin Treatments
Skin treatments is the range of practices that support skin integrity including nutrition, avoidance of excessive sun exposure, and appropriate use of emollients; that enhance appearance such as use of cosmetics, botulinum, exfoliation, fillers, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, peels, retinol therapy; and that remediate skin break down and relieve skin conditions.Skin care is a routine daily procedure in many settings, such as skin that is either too dry or too moist, and prevention of dermatitis and prevention of skin injuries. Skin care is a component in wound healing, neonates, elderly, stomas, radiation treatment and with some medications.
